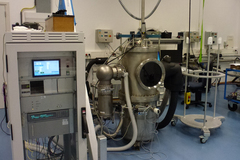
To develop liquified gas storage solutions or predict temperature distribution in a structure early in the design process, the thermal conductivity of the materials used must be known. As this characteristic varies greatly at different temperatures, we can use our setup to determine the thermal conductivity at temperatures between -263°C (10K) to 17°C.
To reach such low temperatures, the setup is vacuum isolated. The setup is highly adaptable and can be modified for different sample geometries up to a length of 300 mm and a diameter of 50 mm and for good or poor thermal conducting (e.g. insulation) materials.
Our measurement method is a method developed by NASA and is described here: James Tuttle, Edgar Canavan, and Amir Jahromi. Cryogenic thermal conductivity measurements on candidate materials for space missions. Cryogenics, 88:36–43, 2017.
Application:
• cryogenic thermal conductivity
• temperature between -263°C (10K) and 17°C e.g. -196 (77K) for liquid nitrogen applications and -183°C (90K) for LNG and liquid oxygen applications
Device under test:
• coupons or subassemblies
• flexible sample geometry
• standard geometry length 100 mm, rectangular crosssection 20 mm
• max. length 300 mm, max. diameter 50 mm
• high and poor thermal conducting materials
• insulation material